Why Metal Building Engineering Plans Are Your Project's Foundation
Metal building engineering plans are the comprehensive technical documents that ensure your structure is safe, code-compliant, and permit-ready. These plans are your project's instruction manual and safety certificate combined, typically including:
- Stamped structural drawings sealed by a licensed engineer.
- Foundation plans with anchor bolt layouts and concrete specifications.
- Design calculations proving each component can handle required loads.
- Erection drawings for step-by-step assembly.
- Load specifications for wind, snow, and seismic requirements.
Without these plans, most building departments won't issue a permit. With them, you have confidence that your metal building will stand strong for decades.
While some jurisdictions may have been lenient in the past, more and more counties now require detailed engineering documentation for building kits. This shift makes understanding these plans more critical than ever.
The costs vary significantly based on what you need. Stamped drawings typically run around $750, while complete design calculations can cost $1,200 or more, and foundation plans add another $1,250. Since not every project requires every document, checking with your local permit authority before you buy can save you significant money and prevent delays.
With our extensive construction and design experience, we've seen many property owners struggle with the engineering documentation process. That's why we created this guide to break down exactly what you need to know, so you can approach your project with confidence and avoid costly permitting delays.
Deconstructing the Blueprint: What's Inside Your Engineering Plans?
Your metal building engineering plans are more than just paperwork; they are the complete instruction manual, safety certificate, and construction roadmap for your project. These documents translate your vision into a language that contractors and building officials understand, providing mathematical proof that your structure is built to last. By guiding your construction crew while also satisfying permit requirements, these plans ensure your project moves forward smoothly.

Understanding Your Metal Building Engineering Plans Package
A complete set of metal building engineering plans contains several distinct documents, each playing a vital role. Understanding what's in the package helps you know what you're paying for and what your building inspector expects.
Erection drawings are your assembly roadmap, showing precisely how every beam, column, and girt connects. They detail the assembly sequence and component placement, guiding your crew during installation.
Anchor bolt plans are the critical link between your building and its foundation, specifying the exact location, size, and depth of every anchor bolt. Precision here is crucial to ensure proper building alignment.
Cross-sectional views are like a slice of your building, revealing how components like insulation and wall panels fit together. They clarify material thicknesses and critical connection details.
Design calculations, often over 100 pages, contain the mathematical proof that every component can handle its required loads. They calculate stress and deflection for all structural elements, and while not always required, stricter jurisdictions demand them to verify the building's safety.
Foundation plans detail your entire foundation system, whether it's a slab, footings, or piers. They specify concrete strength, rebar placement, and slab thickness, providing the blueprint for the structure's base.
Stamped documents bear the seal of a licensed professional engineer, signifying that they have reviewed the plans, verified the calculations, and taken professional responsibility for the design. This stamp is non-negotiable for most building departments.
The Language of Construction: CSI Specs and AutoCAD Details
Understanding the format of your plans helps you work more effectively with design professionals.
The CSI 3-Part Format is the industry standard for organizing construction specifications into three sections: General, Products, and Execution. This standardized format reduces confusion and ensures everyone interprets requirements the same way. Many manufacturers provide specifications in this format, which can be easily integrated into your project's documents.
AutoCAD compatible files(like DWG or DWF) allow architects and engineers to import building details directly into their design software. This streamlines collaboration and reduces errors by integrating the metal building with site plans, architectural drawings, and MEP (mechanical, electrical, plumbing) systems. Instead of redrawing, teams can use manufacturer-provided files for details like cross-sections and connections. For a deeper dive, the Metal Building Systems Design And Specifications resource offers comprehensive guidance.
Pre-Engineered vs. Conventional: Choosing the Right Structural System
When planning a metal building, you'll choose between three main structural systems: pre-engineered, conventional steel, or a hybrid. Each has distinct advantages in cost, speed, and design flexibility.
Pre-engineered metal buildings (PEMBs) are efficiency champions. Components are fabricated off-site to exact specifications and arrive ready to bolt together. This factory-based approach leads to predictable timelines, controlled costs, and reliable quality. Specifying a PEMB in your metal building engineering plans prioritizes speed and efficiency.
Conventional steel buildings offer a custom-built approach. Components are often fabricated for the specific project, involving more on-site welding and construction. This method is ideal for complex architectural features like dramatic curves or unusual angles. The tradeoff is typically a longer timeline and higher cost.
Hybrid systems combine the best of both worlds. They might use pre-engineered frames for the main structure while incorporating conventional steel for unique architectural elements. This approach balances cost-effectiveness with design flexibility.
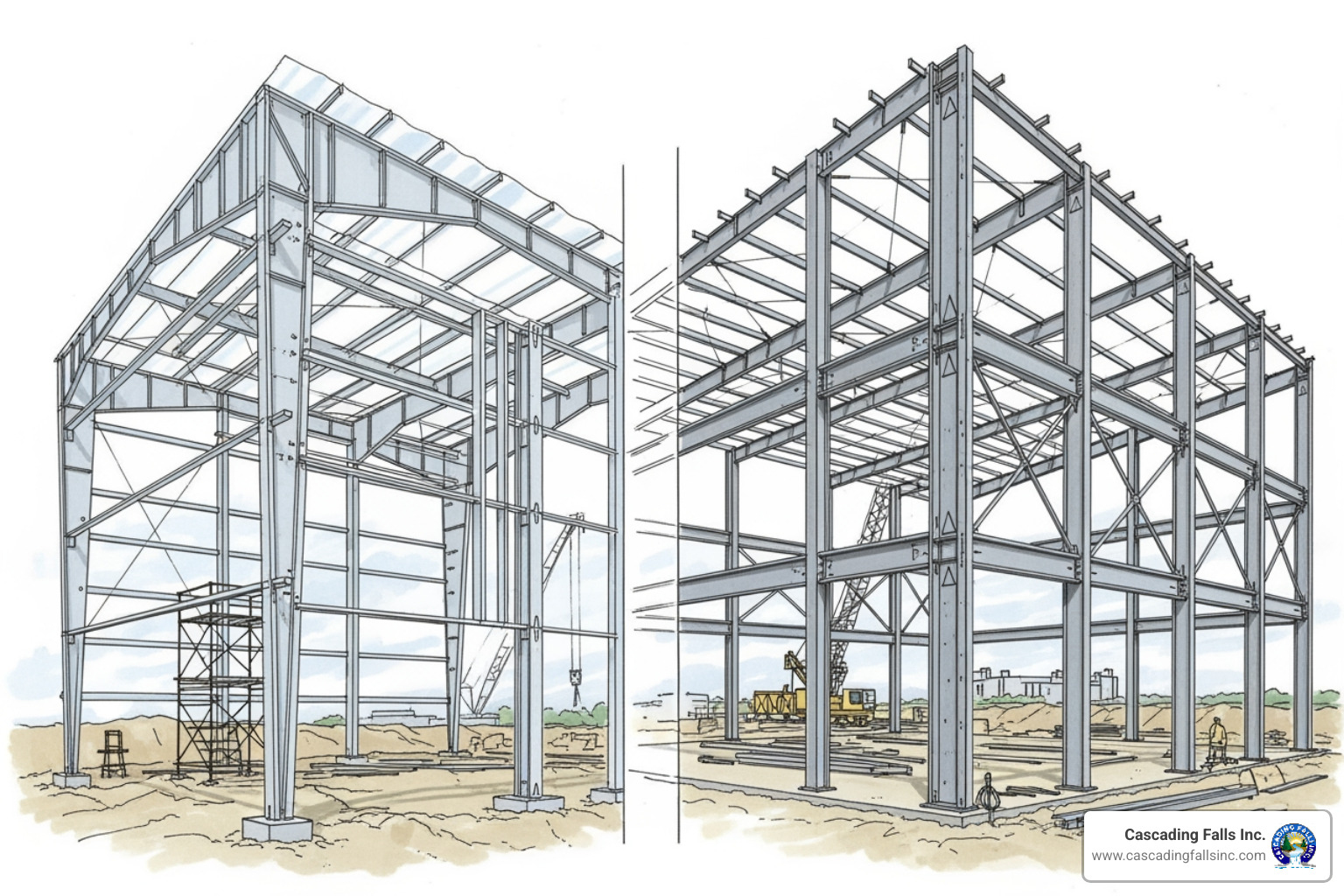
The Anatomy of a Rigid Frame (Red Iron) Building
"Red iron" buildings refer to rigid frame systems, known for their strength and ability to create wide-open interior spaces. The name comes from the reddish-brown primer used on the steel.
The system's strength comes from its primary framing of massive columns and rafters, typically welded I-beams. These create rigid connections that resist lateral forces from wind and seismic events, a critical feature for California construction.
Secondary framing, including girts(for walls) and purlins(for the roof), supports the exterior panels and transfers loads to the primary frame. Engineering plans detail their placement and bracing to ensure structural integrity.
Bracing systems are essential for stability, especially in areas with high winds and seismic activity. These include diagonal rod bracing, flange bracing to prevent buckling, and portal frames for open bays.
The key advantage of rigid frames is their clear span capability, allowing for vast interior spaces without support columns. This makes them ideal for warehouses, manufacturing plants, aircraft hangars, and large retail centers where open floor plans are essential.
The Rise of Cold-Formed Steel and C-Channel Buildings
In contrast to heavy-duty rigid frames, cold-formed steel (or C-channel) buildings are a lighter, more economical option for projects that don't require massive clear spans.
C-channel construction uses steel formed into a "C" shape at room temperature. Often used back-to-back for strength, this method is common in DIY-friendly kits for buildings 35 feet wide or smaller, making it a cost-effective solution for garages and workshops.
These buildings are popular for being DIY-friendly. Kits often include clear, illustrated instructions and simplified hardware (sometimes a single bolt size), allowing for faster assembly and significant savings on labor costs.
However, C-channel systems have limitations. They rely on diaphragm bracing, where wall and roof panels provide structural stability. This typically restricts designs to gable-style roofs and can be a constraint in areas with high snow or seismic loads. Numerous sidewall openings can also compromise this bracing, limiting design flexibility.
To summarize: Rigid frame (red iron) buildings are best for large-scale industrial or commercial projects requiring wide clear spans and high load capacity. They offer design flexibility but come at a higher cost and require professional installation. Cold-formed (C-channel) buildings are economical, DIY-friendly solutions for smaller structures like garages and workshops, with spans typically under 35 feet. They are simpler but have design and load limitations. Your choice depends on your project's scale, budget, and functional needs, with hybrid systems offering a middle ground.
The Critical Role of Metal Building Engineering Plans in Permitting and Safety
Metal building engineering plans are critical for safety and permitting, especially in California. They are the result of an engineer's complex structural analysis and load calculations, ensuring every component can withstand decades of stress from forces like wind, snow, and seismic activity. This detailed engineering is the foundation of your building's safety and longevity, changing a design into a structure that can handle real-world conditions.

Code compliance is a crucial part of the engineering process. It ensures your building meets minimum safety standards, protecting your investment and the people who use the structure.
The Gold Standard: MBMA and Building Code Compliance
The Metal Building Systems Manual from the Metal Building Manufacturers Association (MBMA) is the industry's gold standard. It translates general building codes like the International Building Code (IBC) and ASCE 7 into specific applications for metal building design. For projects in California, where codes are based on the IBC, this manual is an invaluable resource for ensuring compliance.
The manual provides detailed guidance on calculating wind loads, which vary by location; snow loads, which are a factor in higher elevations; and seismic loads, which are fundamental to all California construction. It offers specific design approaches to ensure metal buildings can safely withstand seismic events. You can learn more from this MBMA Manual overview.
The Engineer's Stamp: Your Key to Approval
The engineer's stamp is the final seal of approval on your plans. When a licensed professional engineer stamps your drawings, they are taking professional liability for the design's safety and code compliance. For building officials, this stamp signifies that a qualified expert has performed the necessary structural verification, streamlining the review process.
Stamped drawings are key to expedited permits. Building officials trust the engineer's verification, which prevents delays and rejections. Beyond permitting, the stamp provides peace of mind, confirming your building's long-term safety and structural integrity. At Cascading Falls Inc., we steer this process for you, working with licensed engineers to ensure your project in California receives the professional verification it needs. Our "Whatever It Takes..." approach means we guide you every step of the way.
Navigating Permits, Codes, and Costs
From our years in construction, we've learned that the biggest project headaches often stem from one missed step: consulting the local building authority before purchasing a metal building kit. We've seen clients face unexpected documentation costs or design conflicts because requirements in areas like Roseville and Sacramento can vary significantly between jurisdictions. A simple phone call to your local building department to confirm their specific permit requirements can save you months of delays and thousands of dollars. It's the single most effective way to keep your project on track.
The Cost of Stamped Metal Building Engineering Plans
Understanding the costs of metal building engineering plans is crucial for budgeting. Here's a typical breakdown:
- Stamped drawings: The baseline for most permits, these engineer-stamped plans certify your building's design meets code. Expect to pay around $750.
- Design calculations: Some counties require these detailed documents (often 100+ pages) that mathematically prove the structural integrity of every component. This service typically costs around $1,200.
- Foundation plans: Engineer-stamped plans for your foundation will cost about $1,250. These are critical, as the foundation supports the entire structure.
- Coordination fee: If you use a local engineer for the foundation, they'll need column reaction data from the building manufacturer's engineer. This information transfer usually costs around $300.
While these costs add up, investing in proper engineering upfront prevents far more expensive problems like permit rejections, construction delays, and safety failures.
Key Considerations for Foundation Design
A solid foundation is non-negotiable, and local expertise is key to getting it right. Here are the main factors:
- Soil conditions: Soil types vary greatly, even within Sacramento County. A local engineer understands how regional soils behave and will design a foundation accordingly.
- Frost line: Even in California's Central Valley, frost heave can be a concern. A local engineer will ensure your foundation footings are placed at a safe depth.
- Column reactions: The building manufacturer provides this data, which specifies the load each column transfers to the foundation. Your foundation engineer uses these numbers to design a base that won't crack or settle.
- Anchor bolt settings: The precise placement of anchor bolts is critical for connecting the steel frame to the concrete. Mistakes here can compromise the entire structure.
For these reasons, we recommend hiring a local engineer for your foundation design. They bring invaluable knowledge of local codes in places like Roseville and Sacramento, soil conditions, and can help streamline the permitting process. Most metal buildings use a reinforced concrete slab, and a local expert will ensure the design details—slab thickness, reinforcement, and footings—are perfect for your site. At Cascading Falls Inc., we know a well-designed foundation is the key to a successful project. Learn more about how we can help on our services page.
Frequently Asked Questions about Metal Building Plans
Over the years, we've walked hundreds of property owners through the metal building process. The same thoughtful questions come up time and again—questions that deserve clear, honest answers. Let's tackle the most common ones.
What are "design calculations" and why would I need them?
Design calculations are detailed documents, often over 100 pages, that provide the mathematical proof of your building's structural integrity. They analyze how every component in your metal building engineering plans —from beams to bolts—will perform under specific loads like wind, snow, and seismic forces. While not all jurisdictions require them, stricter counties, particularly in California, often demand these calculations to verify the building's safety. If your building department asks for them, they are mandatory for permit approval. The result is ironclad proof that your structure is engineered to last.
Can I use a local engineer for my foundation plans?
Yes, and we highly recommend it. While your building manufacturer's engineer designs the steel frame, a local engineer provides invaluable expertise for the foundation. They have intimate knowledge of local soil conditions, frost lines, and building codes in areas like Roseville and Sacramento. The process is a collaboration: the building engineer provides the "column reactions" (load data), and the local engineer uses that data to design a foundation perfectly suited to your specific site. This approach is both cost-effective and ensures your foundation is optimized for local conditions and compliant with all regulations.
How does a pre-engineered kit facilitate DIY installation?
Pre-engineered kits are designed for straightforward DIY installation. Key features include:
- Pre-cut and pre-drilled components: Every piece arrives ready for assembly, eliminating the need for on-site cutting or drilling and ensuring a perfect fit.
- Simplified hardware: Many kits use a single bolt size for the entire structure, simplifying the process.
- Illustrated instructions: Detailed, step-by-step visual guides make assembly easy to follow.
This design allows a capable DIYer to erect a building in a matter of days, saving significantly on labor costs. However, if you need assistance, Cascading Falls Inc. is here to help with everything from guidance to full installation, ensuring your project is completed correctly.
Conclusion: Building Your Vision on a Solid Foundation
We've covered the essential role of metal building engineering plans, from stamped drawings to detailed calculations. These documents are not just for permits; they are the blueprint for a safe, durable, and code-compliant structure that will last for decades. Understanding these plans puts you in control of your project, whether it's a workshop in Roseville or a commercial facility in Sacramento.
The investment in professional engineering pays for itself by ensuring long-term safety, protecting your financial investment, and preventing costly delays. While there are costs for stamped plans and calculations, they are minor compared to the expense of fixing structural problems or dealing with permit rejections. A quick call to your local building authority before you buy can clarify exactly what you need.
Navigating the engineering and permitting process can be daunting. At Cascading Falls Inc., our "Whatever It Takes..." approach means we guide you through every step. We are committed to helping you build your vision on a solid foundation.
Ready to start your metal building project? Let us help you manage the engineering process and bring your plans to life with quality craftsmanship.






